How to setup Apache VirtualHost in MacOSX 10.9 Step by Step [ How To ]
VirtualHost is a term that refers to hosting multiple websites on the same web server, like hosting “example.com” and “example.org” on the same server. In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to set up a Name-Based Virtual server in macOS. You just have to configure your hosts file to map each hostname to the same IP address and then configure the Apache HTTP Server to recognize the different hostnames.
Note: macOS X Mavericks (10.9) is very outdated. For modern macOS versions, the Apache configuration path and methods may differ. Also, macOS now uses systemd or launchd for service management instead of apachectl in some cases.
Just follow simple Steps .
Enable Virtual Hosts
Open “ /etc/apache2/httpd.conf ”
open terminal
sudo nano /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
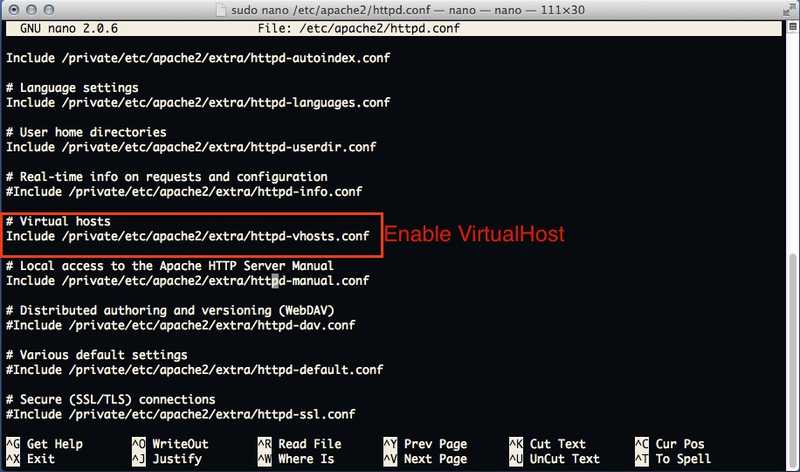
Find Virtual Host include line and Uncomment ( remove # sign from front ) that line
# Virtual hosts
Include /private/etc/apache2/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf
Setup Virtual Host
Save that file . and open /etc/apache2/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf File
“
NameVirtualHost *:80 <VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin admin@example.com DocumentRoot "/Users/alok/Sites/example" ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com ErrorLog "/private/var/log/apache2/example.com" CustomLog "/private/var/log/apache2/example.com" common # Other directives here <directory "/Users/alok/Sites/example"> Options Indexes MultiViews FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> </VirtualHost>
setup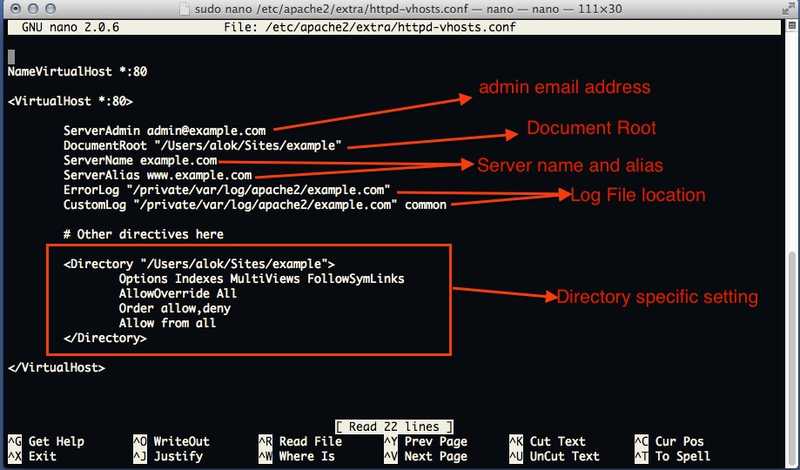
Now setup Host File to point at localhost as example.com
open /etc/hosts
sudo nano /etc/hosts
and add 127.0.0.1 example.com
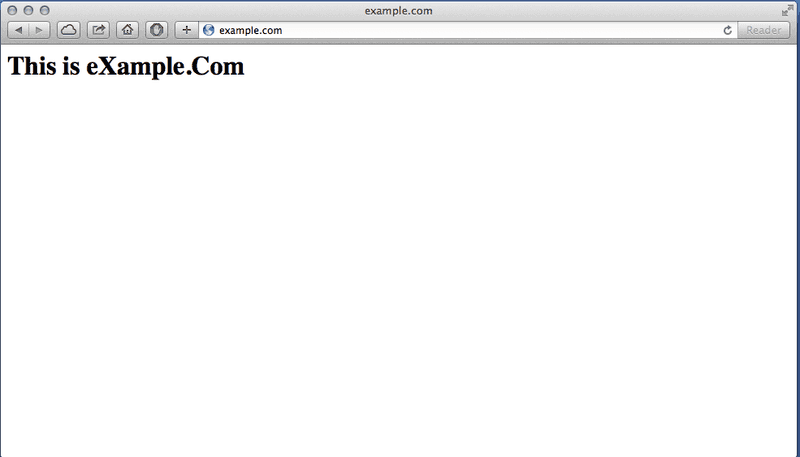
And restart the web server. Open Terminal and type sudo apachectl restart, then open your browser and navigate to example.com. Now example.com will point to your local web server.
Note: On modern macOS versions, you might need to use sudo brew services restart httpd if you installed Apache via Homebrew, or use System Preferences to manage the service.
For any kind of discussion and help, join our forum.